A dive into the Model Context Protocol (MCP) by Anthropic
A look at MCP servers, along with an example implementation in Python
Published on May 4 2025 at 6:07pm
Overview
This page introduces the Model Context Protocol (MCP). MCP is a protocol to provide context to a Large Language Model. LLMs are all the rage at the moment, with a large number of high quality open source LLMs now available with permissive licensing. MCPs are a great way to extend the capabilities of LLMs to access data and services, acting as a bridge between the LLM and the services it needs to access.
Architecture and Components
Architecture
flowchart LR
Client[MCP Client] -->|MCP Request| Server[MCP Server]
Server -->|Query| LocalDB[(Local Data Source)]
LocalDB -->|Results| Server
Server -->|MCP Request| RemoteServer[Remote MCP Server]
RemoteServer -->|Query| RemoteService[Remote Service]
RemoteService -->|Results| RemoteServer
RemoteServer -->|MCP Response| Server
Server -->|MCP Response| Client
Fig. The architecture of the Model Context Protocol
An MCP Client - that sends requests using the Model Context Protocol to an MCP Server
The MCP Server - which accesses a local data source for information and makes MCP requests to another remote MCP server when needed
The Remote MCP Server - that communicates with a remote service returns responses back to the original MCP server
Note: An MCP Host (Claude desktop, IDEs etc.) access data via MCP clients and MCP servers.
Key Components
sequenceDiagram
participant Host as MCP Host
participant Client as MCP Client
participant Local as Local MCP Server
participant Remote as Remote MCP Server
Host->>Client: 1. User Request
Client->>Local: 2. Process Request
Local-->>Client: 3. Local Response
Client->>Remote: 4. Additional Context
Remote-->>Client: 5. Remote Response
Client-->>Host: 6. Combined Response
Fig. The key components of the Model Context Protocol architecture
The flow illustrates the basic chain of communication in the Model Context Protocol ecosystem, showing how MCP enables standardized access to both local and remote data sources through a consistent protocol.
MCP Server Development
Lets dive straight in, and try and build a MCP server, that does something simple - access Stock information. Here’s what we are trying to accomplish -
graph TD
MCP_Host -->|Request| LLM
LLM -->|Processed Request| MCP_Server(Stocks)
MCP_Server(Stocks) -->|Request| Remote_Service(Yahoo Stocks API)
Remote_Service(Yahoo Stocks API) -->|Response| MCP_Server(Stocks)
MCP_Server(Stocks) -->|Response| LLM
LLM -->|Final Response| MCP_Host
Fig. Simple Stocks MCP Server
The key elements here are the actual server which we will develop, and the Yahoo Stocks API (external service). We access the Stocks API via a standard protocol, and the MCP server which we are about to build will help us accomplish this.
To keep things simple, we will develop a MCP server which supports a get_stock_data(ticker) function only.
Creating Stocks API (based on Yahoo Stocks API)
Install required libraries
pip install flask requests
Stocks API source code
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import requests
import time
import random
import logging
from functools import lru_cache
# Configure logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger('stock_api')
app = Flask(__name__)
# Yahoo Finance API endpoint for stock chart data
def get_chart_url(ticker):
return f"https://query1.finance.yahoo.com/v8/finance/chart/{ticker}?range=1d&interval=1d"
def get_stock_price(ticker):
"""
Fetch stock chart data from Yahoo Finance API by properly mimicking a browser request.
"""
# No query parameters needed in URL as they're now part of the URL itself
url = get_chart_url(ticker)
# Comprehensive browser-like headers - this is critical to avoid 429 errors
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate, br",
"Referer": "https://finance.yahoo.com/",
"sec-ch-ua": '"Google Chrome";v="120", "Chromium";v="120", "Not-A.Brand";v="99"',
"sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0",
"sec-ch-ua-platform": '"Windows"',
"sec-fetch-dest": "document",
"sec-fetch-mode": "navigate",
"sec-fetch-site": "same-origin",
"Cache-Control": "max-age=0",
"Connection": "keep-alive"
}
try:
# Use a new session for each request to avoid cookie tracking issues
with requests.Session() as session:
# First visit the base page to get cookies (like a real browser would)
session.get("https://finance.yahoo.com/", headers=headers)
# Then make the actual API request
response = session.get(url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
# Extract data from chart response structure
chart_result = data.get("chart", {}).get("result", [])
if not chart_result:
return {"error": f"Chart data not found for {ticker}"}
quote = chart_result[0].get("meta", {})
indicators = chart_result[0].get("indicators", {})
# Get the latest price from quote
current_price = quote.get("regularMarketPrice")
if current_price is not None:
return {
"ticker": ticker,
"price": float(current_price),
"currency": quote.get("currency", "USD"),
"exchange": quote.get("exchangeName", ""),
"timestamp": quote.get("regularMarketTime", 0)
}
else:
return {"error": f"Price data not found for {ticker}"}
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
logger.error(f"Request failed: {str(e)}")
return {"error": f"API request failed: {str(e)}"}
except (KeyError, IndexError, ValueError) as e:
logger.error(f"Error parsing response: {str(e)}")
return {"error": f"Failed to parse API response: {str(e)}"}
@app.route("/get_stock_data", methods=["GET"])
def handle_get_stock_data():
ticker = request.args.get("ticker")
if not ticker:
return jsonify({"error": "Missing 'ticker' parameter"}), 400
result = get_stock_price(ticker)
# Return appropriate status code based on result
if "error" in result and "not found" in result["error"]:
return jsonify(result), 404
elif "error" in result:
return jsonify(result), 500
return jsonify(result)
@app.route("/health", methods=["GET"])
def health_check():
"""Simple health check endpoint"""
return jsonify({"status": "healthy"})
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="0.0.0.0", port=5566, debug=True)
Usage
You can use and test this server in the foll. manner -
- Start the server
python mcp_server.py
- Test with curl
curl "http://localhost:5566/get_stock_data?ticker=AAPL"
So far we’ve created an API /get_stock_data which accepts a ticker and returns stock price information. Now we move on to adding MCP support.
Implementing the MCP protocol
To add this as an MCP (Model Control Protocol) server for Claude Desktop, we need to implement the MCP protocol in our Flask application.
Updated Stocks API source code
Ok, I need to complain a little. I had this annoying issue with Flask putting out debug output which was messing up the Claude desktop MCP parsing. I was about to give up for the day, but Claude AI suggested I try waitress. I updated the code to use waitress to avoid putting out any debug output. Voila it works.
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import requests
import logging
import json
import time
import sys
import os
import socket
from waitress import serve
# Completely disable all logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.CRITICAL)
logger = logging.getLogger('mcp_stock_server')
logger.disabled = True
# Create Flask app with minimal configuration
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['JSONIFY_PRETTYPRINT_REGULAR'] = False
app.config['JSON_SORT_KEYS'] = False
# Disable all Flask logging
app.logger.disabled = True
log = logging.getLogger('werkzeug')
log.disabled = True
def is_port_in_use(port):
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
return s.connect_ex(('localhost', port)) == 0
def find_available_port(start_port):
port = start_port
while is_port_in_use(port):
port += 1
return port
# Yahoo Finance API endpoint for stock chart data
def get_chart_url(ticker):
return f"https://query1.finance.yahoo.com/v8/finance/chart/{ticker}?range=1d&interval=1d"
def get_stock_price(ticker):
"""
Fetch stock chart data from Yahoo Finance API by properly mimicking a browser request.
"""
# No query parameters needed in URL as they're now part of the URL itself
url = get_chart_url(ticker)
# Comprehensive browser-like headers - this is critical to avoid 429 errors
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"Accept": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7",
"Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.9",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate, br",
"Referer": "https://finance.yahoo.com/",
"sec-ch-ua": '"Google Chrome";v="120", "Chromium";v="120", "Not-A.Brand";v="99"',
"sec-ch-ua-mobile": "?0",
"sec-ch-ua-platform": '"Windows"',
"sec-fetch-dest": "document",
"sec-fetch-mode": "navigate",
"sec-fetch-site": "same-origin",
"Cache-Control": "max-age=0",
"Connection": "keep-alive"
}
try:
# Use a new session for each request to avoid cookie tracking issues
with requests.Session() as session:
# First visit the base page to get cookies (like a real browser would)
session.get("https://finance.yahoo.com/", headers=headers)
# Then make the actual API request
response = session.get(url, headers=headers)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
# Extract data from chart response structure
chart_result = data.get("chart", {}).get("result", [])
if not chart_result:
return {"error": f"Chart data not found for {ticker}"}
quote = chart_result[0].get("meta", {})
# Get the latest price from quote
current_price = quote.get("regularMarketPrice")
if current_price is not None:
return {
"ticker": ticker,
"price": float(current_price),
"currency": quote.get("currency", "USD"),
"exchange": quote.get("exchangeName", ""),
"timestamp": quote.get("regularMarketTime", 0)
}
else:
return {"error": f"Price data not found for {ticker}"}
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
logger.error(f"Request failed: {str(e)}")
return {"error": f"API request failed: {str(e)}"}
except (KeyError, IndexError, ValueError) as e:
logger.error(f"Error parsing response: {str(e)}")
return {"error": f"Failed to parse API response: {str(e)}"}
# Original stock data endpoint
@app.route("/get_stock_data", methods=["GET"])
def handle_get_stock_data():
ticker = request.args.get("ticker")
if not ticker:
return jsonify({"error": "Missing 'ticker' parameter"}), 400
result = get_stock_price(ticker)
# Return appropriate status code based on result
if "error" in result and "not found" in result["error"]:
return jsonify(result), 404
elif "error" in result:
return jsonify(result), 500
return jsonify(result)
# MCP Protocol Implementation
@app.route("/mcp", methods=["POST"])
def mcp_endpoint():
try:
# Parse the incoming request
mcp_request = request.json
# Check for required fields in MCP request
if not mcp_request or "messages" not in mcp_request:
return jsonify({
"error": "Invalid MCP request format"
}), 400
# Extract the latest user message
user_messages = [msg for msg in mcp_request["messages"] if msg.get("role") == "user"]
if not user_messages:
return jsonify({
"error": "No user message found in request"
}), 400
latest_user_message = user_messages[-1]["content"]
# Process the user message to extract ticker symbol
# This is a simple implementation - you might want to add more sophisticated parsing
ticker = None
# Check if message contains stock price query format
words = latest_user_message.lower().split()
# Look for patterns like "price of AAPL" or "AAPL stock price" or "stock price for AAPL"
for i, word in enumerate(words):
if word.upper() == word and len(word) >= 1 and len(word) <= 5 and word.isalpha():
# This looks like a ticker symbol (all caps, 1-5 letters)
ticker = word.upper()
break
if i < len(words) - 1:
if (word == "for" or word == "of") and words[i+1].upper() == words[i+1] and len(words[i+1]) <= 5:
ticker = words[i+1].upper()
break
# If we couldn't find a ticker in the message
if not ticker:
return jsonify({
"messages": [{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I couldn't identify a stock ticker symbol in your message. Please specify a valid stock symbol like AAPL, MSFT, or TSLA."
}]
})
# Get stock data
stock_data = get_stock_price(ticker)
# Format the response for Claude Desktop
if "error" in stock_data:
response_content = f"I encountered an error looking up {ticker}: {stock_data['error']}"
else:
# Format price with 2 decimal places
price = f"{stock_data['price']:.2f}"
response_content = f"The current price of {ticker} is {price} {stock_data['currency']} on {stock_data['exchange']}."
# Return response in MCP format
return jsonify({
"messages": [{
"role": "assistant",
"content": response_content
}]
})
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"MCP processing error: {str(e)}")
return jsonify({
"messages": [{
"role": "assistant",
"content": f"I encountered an error processing your request: {str(e)}"
}]
})
@app.route("/health", methods=["GET"])
def health_check():
"""Simple health check endpoint"""
return jsonify({"status": "healthy", "service": "MCP Stock Server"})
# MCP Info endpoint to provide information about this MCP server
@app.route("/mcp/info", methods=["GET"])
def mcp_info():
return jsonify({
"name": "Stock Price Lookup",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Get real-time stock prices from Yahoo Finance",
"author": "Karan Kadam",
"properties": {
"max_tokens_to_sample": 1000,
"temperature": 0
}
})
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Get port from environment or use default
default_port = 8081
port = int(os.environ.get('PORT', default_port))
# Find an available port if the specified one is in use
if is_port_in_use(port):
port = find_available_port(port)
print(f"Port {port} is available", file=sys.stderr)
# Check if running in Claude Desktop environment
if 'WERKZEUG_SERVER_FD' in os.environ:
try:
# Running in Claude Desktop - use the provided file descriptor
serve(
app,
host="0.0.0.0",
port=port,
threads=1,
_quiet=True,
fd=int(os.environ["WERKZEUG_SERVER_FD"])
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error starting server: {str(e)}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
else:
# Running standalone - use waitress server
serve(
app,
host="0.0.0.0",
port=port,
threads=1,
_quiet=True
)
What This Implementation Includes:
Implements the /mcp endpoint required by Claude Desktop
Handles MCP request format and returns proper MCP responses
Provides /mcp/info endpoint with metadata about your service
Smart Ticker Symbol Detection: a. Tries to identify stock symbols in natural language queries b. Looks for uppercase words that are 1-5 letters long c. Handles common phrases like “price of AAPL” or “AAPL stock price”
Formatted Responses: Returns nicely formatted answers with price, currency and exchange
Integration with a LLM
Lets integrate this server we created with a LLM. I will be using Claude desktop as an example here -
Install Claude for desktop
You can download Claude for desktop here Download
Run the server
Install dependencies and run the server we created -
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install flask requests waitressç
python mcp_server.py
This will start the server on port 8081 if everything worked properly.
Add server to Claude desktop
- Open Claude Desktop
- Go to Settings > Developer
- Click “Edit Config”
- Update the config
claude_desktop_config.jsonas shown below - Restart Claude Desktop
Here is what your claude_desktop_config.json should look like -
{
"serverConfig": {
"command": "/bin/sh",
"args": [
"-c"
]
},
"stock_price_server": {
"command": "python",
"args": [
"mcp_server.py"
],
"env": {
"FLASK_APP": "mcp_server.py",
"FLASK_ENV": "production",
"PORT": "8081"
}
}
}
}
Note: Update the paths according to your machine. Verify that your mcp server is registered and working well under Settings > Developer.
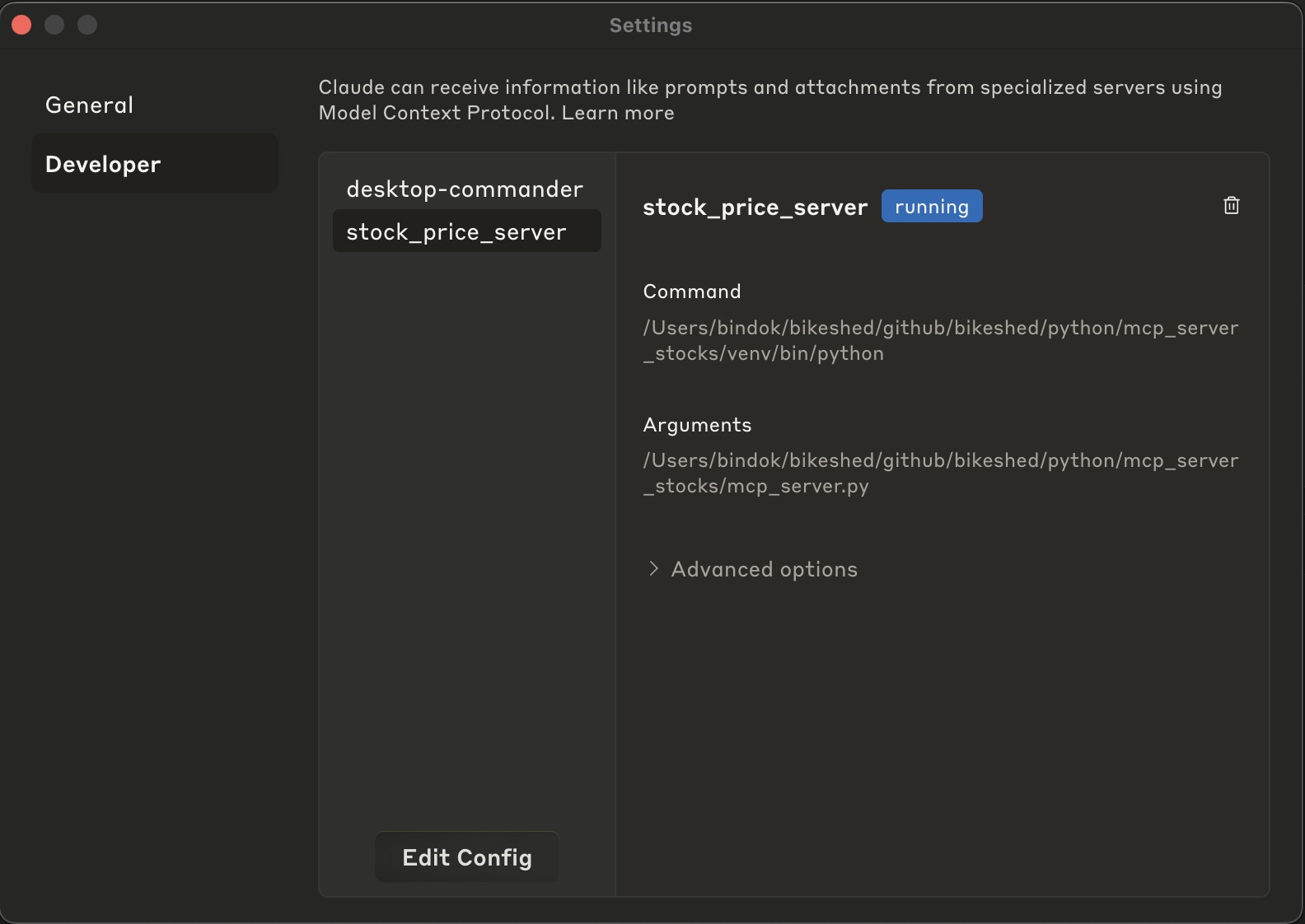
Using the MCP server from Claude desktop
Once connected, you can ask Claude Desktop questions about stock prices like:
"What's the stock price of AAPL?"
"Get me the current stock price for MSFT"
"How much is TSLA stock trading for?"
Claude will recognize these queries and route them to your MCP server, which will fetch the real-time stock data and return it.
Testing and Troubleshooting:
- You can test the stock data API directly at: http://localhost:8081/get_stock_data?ticker=AAPL
- You can check if the server is running at: http://localhost:8081/health
- You can verify the MCP info at: http://localhost:8081/mcp/info
The server keeps your existing stock API implementation intact while adding the MCP functionality on top, so both can be used independently.
MCP is a great way to extend the capabilities of LLMs to access data and services. It is a simple protocol to implement and can be used to access a wide range of data sources. I see myself implementing more MCP servers to access different data sources in the future.
Tags: python , ai , mcp , programming